In a world where life and career decisions are increasingly diverse and complex, fertility preservation emerges as an option for those who wish to keep the doors open to the possibility of motherhood or fatherhood in the future. Whether for medical, professional, or personal reasons, preserving fertility offers a strategic and emotionally significant solution for many people.
How to preserve fertility?
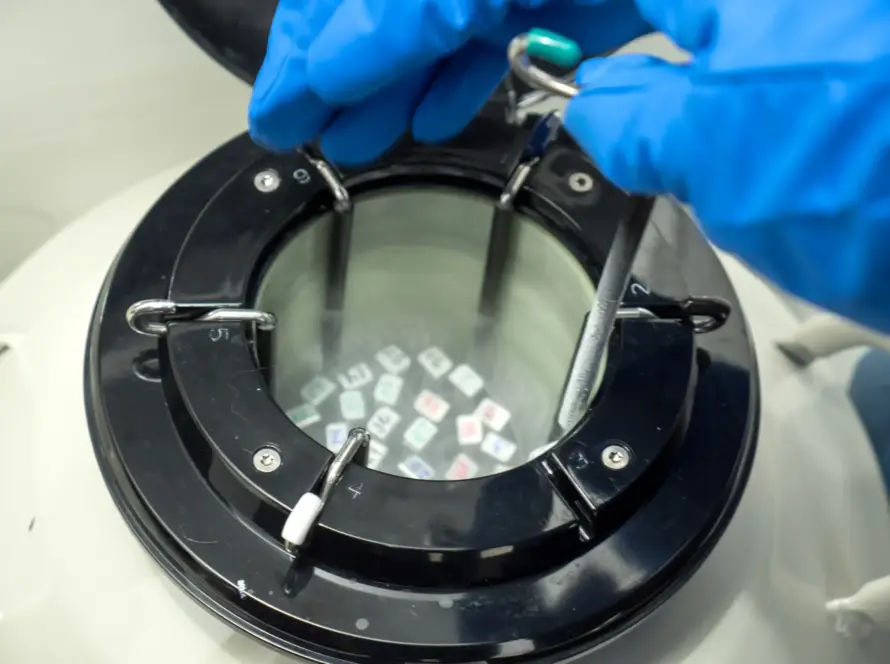
The process of fertility preservation involves the extraction and storage of gametes (eggs or sperm) for future use. For women, this involves a process of ovarian stimulation followed by egg extraction, which is then frozen for later use. For men, fertility preservation involves the collection of sperm samples, which are also frozen for storage. Both procedures are safe and supported by technological advances in reproductive medicine.
When to preserve fertility?
The ideal time to consider fertility preservation may vary depending on individual circumstances, but it is essential to address this issue before options are limited by time or medical conditions. Ideally, the discussion about fertility preservation should take place during the optimal fertile age, generally before the age of 35 for women, as the quality and quantity of eggs decrease with age. However, this does not exclude older people from considering this path with the appropriate guidance from fertility specialists.